WBS or Work Breakdown Structure is defined as “a deliverable oriented hierarchical decomposition of the work to be executed by the project team to accomplish the project objectives and create the required deliverables. It organizes and defines the total scope of the project.” [PMBOK 4th Edition, Glossary pg. 452].
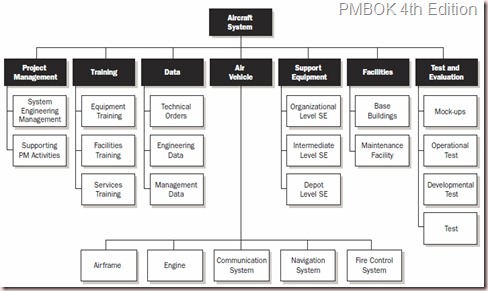
A WBS is essentially a mind-map in the form of tree structure that is structured to achieve the main project deliverable. Here’s how it looks like:
The creation of WBS is so important that it is a process group on its own; Create WBS under the knowledge area Scope Management. To create, we will be using the technique of decomposition. Decomposition means to do a breakdown of project deliverables into smaller and more manageable components. We decompose until we reach a component that we can measure in terms of time and cost. The lowest level in a WBS is called a work package.
Each work package will be tied to a control account. A control account is a management control point where scope, budget, actual cost and schedule are integrated and compared to earned value for performance measurement.
A WBS is accompanied by its WBS Dictionary. This is a document that describes each of the WBS components in detail. It will include a brief description of the deliverables, list of activities, list of milestones, etc.
Project Management is a deliverable on its own. Therefore, it has to be depicted in the WBS as well.
The WBS, WBS Dictionary and the Project Scope Statement; together they form the Scope Baseline. The Scope Baseline is one of the important component of Project Management Plan.
So, what is so important about having a WBS? WBS lets you see the deliverables that needs to be accomplished and the components that needs to be completed to ensure the deliverables can be met. Having work packages at the ready and using it alongside the WBS dictionary will ease the creation of schedule, resources management and cost management.
[Images taken from PMBOK 4th Edition]

No comments:
Post a Comment