In project management, your curves are very important; to you and to your stakeholders. Everyone is interested to know about your S-curve.
What does an S-curve show? It shows where you are from what you have planned. It it shows how much have you spent at a point of time during the life of your project. It shows the performance of your project.
Let me show you a very nice picture of the curves that you might have.
For today, let us get to know the specific areas of the curve (Refer to PMBOK Guide 4th Edition pg.181).
Plan – Planned Value; PV, is what has been planned in the beginning: the authorized budget for the scheduled work to be accomplished. It is also known as Budgeted Cost Work Scheduled; BCWS. In short, the amount that has been planned to pay for the work scheduled.
Earned Value – EV, is the value of work performed based on the budgeted cost for the particular work. It is also known as Budgeted Cost Work Performed; BCWP. In short; the amount that has been planned to pay for the work that has been performed.
Actuals – Actual Cost; AC, is the actual spending on the actual work that has been completed. It is also known as Actual Cost Work Performed. In short, the actual amount incurred for actual work being done.
Cost Variance – CV, a measure of cost performance for the project. Based on the value, we will know whether the project is under budget or over budget.
Schedule Variance – SV, a measure of schedule performance for the project. Based on the value, we will know whether the project is behind or ahead of schedule.
For both variances;
PV > 0 == Ahead of schedule
You could also derive measure of efficiency from these values:
Cost Performance Index – CPI, is the measure of efficiency of the value of work done and how well monies are spent.
Schedule Performance Index – SPI, is the measure of efficiency of time scheduled; it is a measure of progressed achieved compared to progress planned.
The S-curve is a popular representation of Earned Value Management. It is a performance measurement technique that is comparing actual collected values against the baselines that was set at the beginning of the project. It integrates cost, scope and schedule measures in one presentation.
At a point of time, the data for EV, PV and AC is collected for reporting. From the value, the project team will be able to assess the project performance so far. A cumulative data collection will enable the plotting of the S-curve to present the project performance in a graphic view. Note: Include this in your status report to the stakeholders and senior management.
So, if you plot your S-curve for this month, how does it look like?
And you thought when I talked about curves in the beginning, it has nothing to do with project management. Hah!
| NOTE: Earned Value Management is the tools and techniques for the Process Group: Control Costs |
[S-Curve graph is modified from NASA EVM Tutorial: http://evm.nasa.gov/analysis.html]






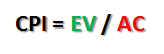
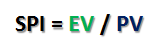
No comments:
Post a Comment